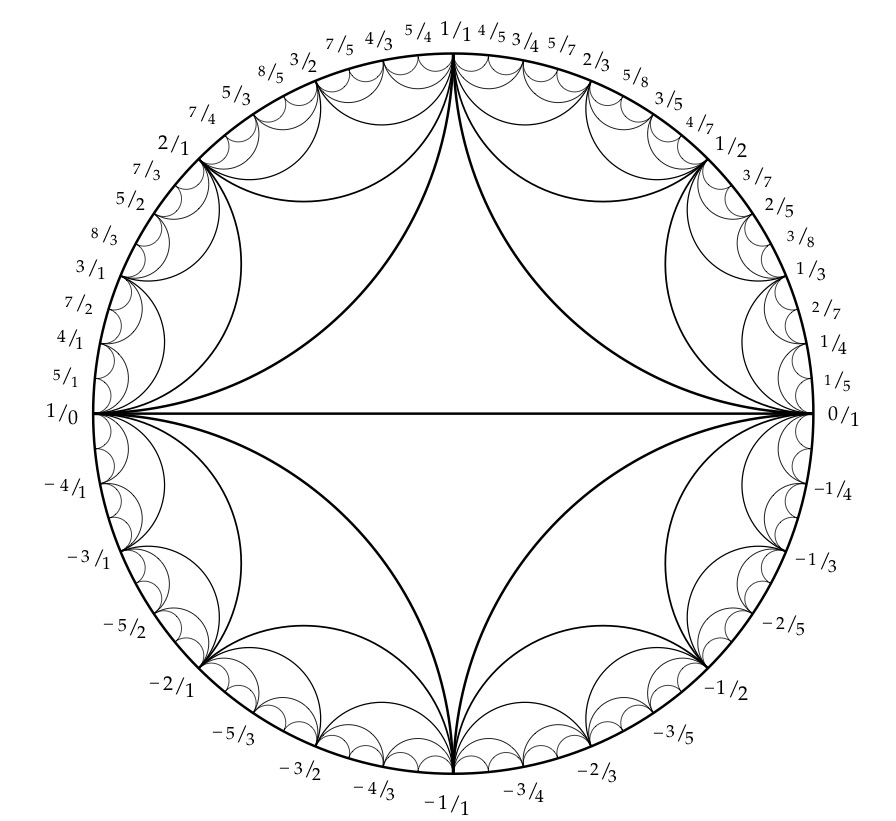
Problem 0

Problem 1
Markoff numbers are integers that appear a Markoff triple
which are solutions of a Diophantine equation
the so-called Markoff cubic
Odd index Fibonacci numbers are Markoff numbers
Frobenius uniqueness conjecture
The largest integer in a triple determines the two other numbers.
- Only partial results
- m = Markoff number = z > y > x
- Jack Button for m prime
- Zhang An elementary proof...
- Lang, Tan A simple proof....
- Baragar m, 3m - 2, 3m + 2 prime
Problem 2:
Give a geometric proof of
If
References etc
- First proof Euler (reciprocity, descent)
- Heath-Brown, Fermat’s two squares theorem. Invariant (1984)
- Zagier, A one-sentence proof that every prime p = 1 (mod 4) is a sum of two squares, 1990
- Dolan, S., The Mathematical Gazette, 106(564). (2021)
- Elsholtz, Combinatorial Approach to Sums of Two Squares and Related Problems. (2010)
Zagier: one sentence
Problem 3:
Martin Aigner
- Proofs from THE BOOK
- 100 years of uniqueness
- Convexity and Aigner's Conjectures
- Prove his conjectures with one figure?
There is a natural map (we'll see why shortly)

Aigner's conjectures proof
Sketch of proof
Definition: Let
Natural map:
Theorem The shortest representative for a non trivial homology class is always a multiple of a closed simple geodesic.
- important
Aigner's conjectures proof

Labeling Markoff numbers
A tale of trees
- Markoff number =
- Farey "tree" of coprime integers
- Markoff tree of solutions to the cubic
- Bass-Serre tree of a free product
- Mapping class group of the torus
coprime integers
- closed geodesic
- arc on a punctured torus(disjoint from the closed geodesic)
- obvious transitive
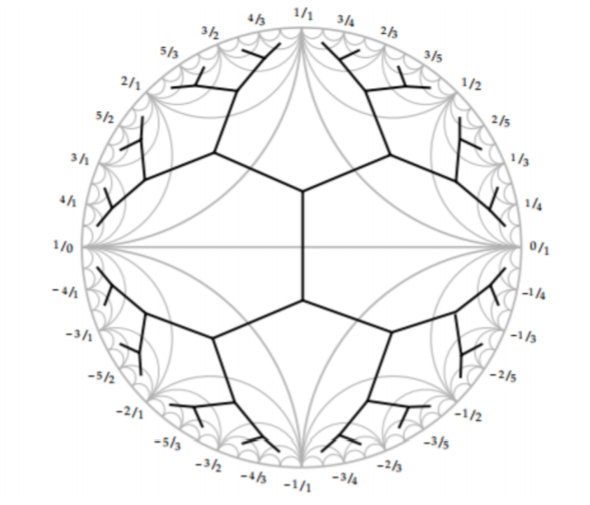
Tree structure
comes from Bass-Serre tree of
Role of the character variety
H. Cohn Approach to Markoff’s Minimal Forms Through Modular Functions (1955)
- modular torus = quotient of upper half plane
- relates Markoff numbers to lengths of simple closed geodesics
- modular torus = quotient of upper half plane
- obtained from a pair of ideal triangles by identification
- elliptic involution swaps triangles fixes midpoint of diagonal
Character variety
modular torus =
- any hyperbolic torus =
- lifts to
- Definition character map
Theorem: (Cohn and many others) The semi-algebraic set:
-
identified with the Teichmueller space of the punctured torus.
-
group of the automorphisms is induced by the action of the mapping class group
-
the permutation
-
the (Vieta) involution
Uniqueness conjecture
- The largest integer in a triple determines the two other numbers.
- The multiplicity of any number in the complementary regions to the tree is at most 6
Simple representatives
- blue curve is simple representative of its homotopy class
- not every homotopy class contains a simple curve
- every (non trivial) homology class has a representative that is a (multiple) of a simple curve
Button's Theorem and
Button's Theorem
If
then there is a unique triple
Theorem (Fermat)
Let
- Button's theorem follows from "unicity" of
- unique factorisation
Frobenius uniqueness conjecture
- The multiplicity of any number in the complementary regions to the tree is at most 6
- loop around the cusp
- automorphism group
- "generator" of the automorphism group is
- := elliptic involution has 3 fixed points which lift to the
- elliptic involution swaps triangles fixes midpoint of diagonal
- the fixed points lift to the

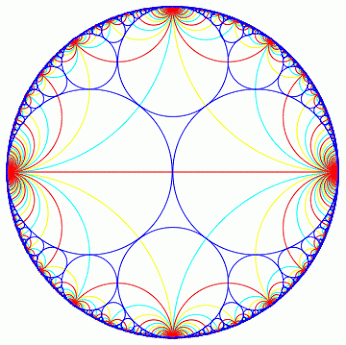
Ford circles
Ford circles
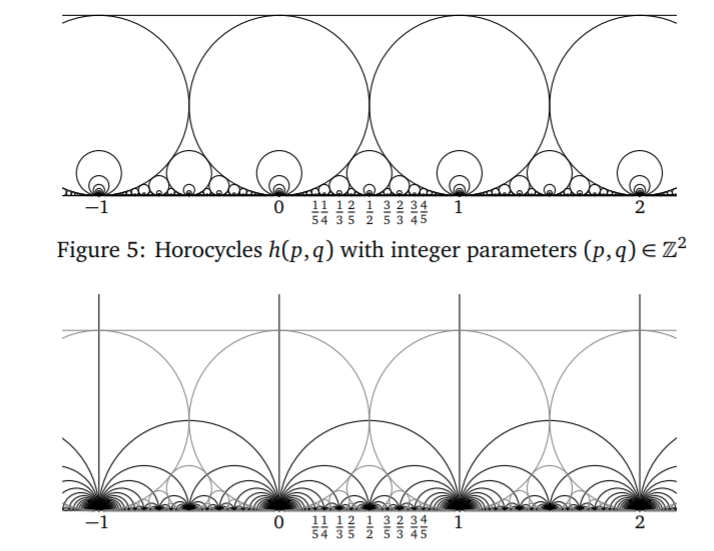
Definitions
arc = Poincaré geodesic joining
-
-
-
-
orbit of

- hyperbolic midpoint of the arc joining
- hyperbolic midpoint of the arc joining
Proposition (Penner)
- arc joining
- can suppose
- joins Ford circle
- hyperbolic length of portion outside these is
pairing arcs and curves
- modular torus obtained from a pair of ideal triangles by identification
- blue arc
Lemma A
The
simple closed geodesic such that
Proof: Easy calculation
Corollary B
Every Markoff number
Geometric proof of corollary
- simple close geodesic
- the unique arc
- since
and so we have the equation
by the same argument....
Lemma C
Let
The "number of ways" of writing
with
Counting solutions
The "number of ways" of writing
- eight solutions
- four choices for the signs
- swap
- only swapping
Example
Lemma C'
The number of ways of writing
is equal to the number of arcs on the modular surface
- of
- which pass through the cone point of of order 2.
exactly 6 simple arcs of
Proof of Button
every Markoff number
- if
Sums of squares
Button's Theorem
If
then there is a unique triple
Theorem F1: Let
has a solution over
iff
Theorem F2: Let
has a solution over
iff
two groups of order 4
Acting on
Acting on
Zagier
Let's begin then...
Burnside Lemma
-
-
-
- proposition
If
then - Follows from Wilson's Theorem
"Geometric" proof: Group acting on
-
Count fixed points
-
identity
-
-
-
Apply Burnside
QED
Theorem F2: sum of 2 squares
Acting on
or on the arcs of
- standard fundamental domain
- = pair of ideal triangles
- all edges
of
- one dotted arc has
- other dotted arc has
Lemma C'
Let
The "number of ways" of writing
with
subgroup of automorphisms
fixing the cusp labeled
- a reflection
swaps
fixes the arc of - another reflection
fixes
fixes the arc of - both fix the midpoint
group lifts to
The set
- arcs joining cusps
- "lift to vertical lines" with endpoints
Fixed points I
First the automorphism
- fixes
- fixes the arc of
- swaps the upper and lower ideal triangles
The automorphism
fixes two and exactly two arcs in
- can thencan then apply Burnside Lemma to prove Theorem F2
- Proof:
- suppose that there is an invariant arc that starts at
- then it must end at
- its
Questions/Remarks
Can other elementary results for quadratic forms?
-
using immersed "equilateral" ideal triangles. -
(Elsholtz)
using arcs -
Baragar ? m, 3m - 2, 3m + 2 prime
-
More detailed analysis of the spectrum of
Orthotree, orthoshapes and ortho-integral surfaces
Nhat Minh Doan